UHMC WATER QUALITY LAB
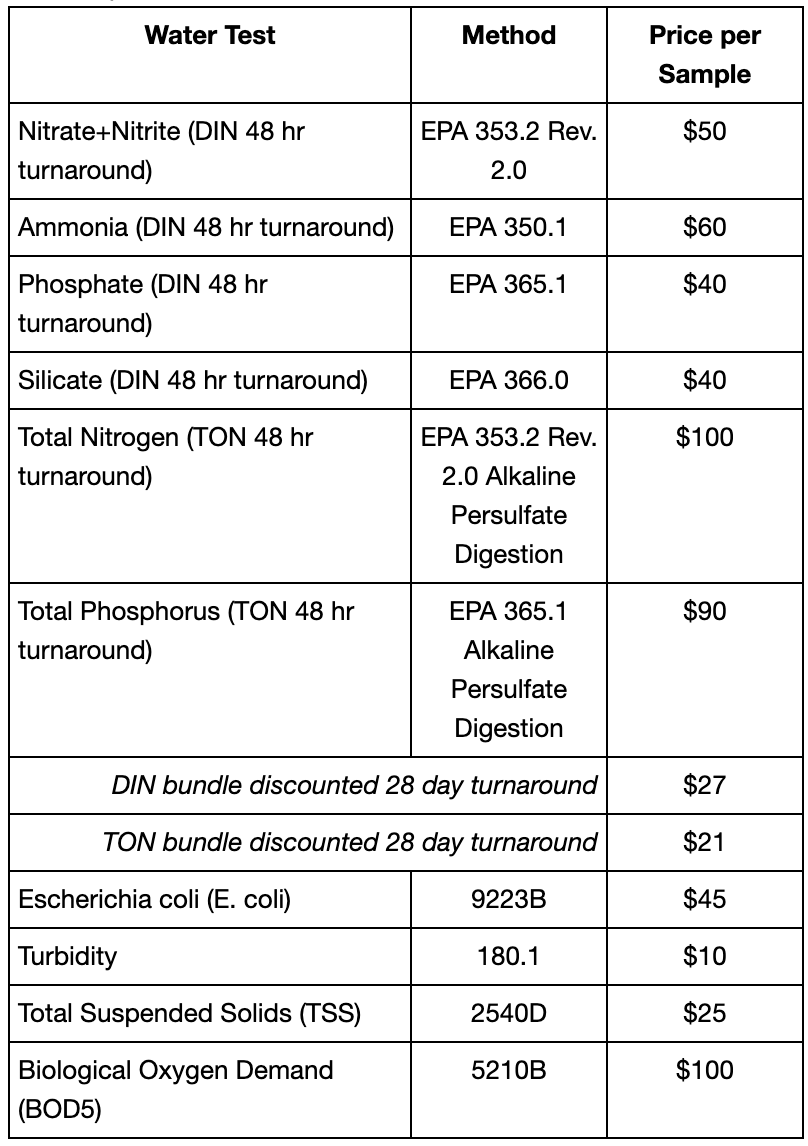
- Inorganic nutrients: nitrate+nitrite, silicate, phosphate, and ammonia
- Organic nutrients: total nitrogen and phosphorus
- Total suspended solids (TSS)
- Turbidity
- Biological oxygen demand (BOD5)
- Escherichia coli (E.coli)
Sample testing is available to all research organizations, industries, and any interested community members.

University of Hawaiʻi Maui College
310 W Kaʻahumanu Ave.
Ike Leʻa Building Rm 123
Kahului, HI 96732
Email: crystal.henkel@hawaii.
METHODS
SEAL AutoAnalyzer 3
The AA3 is a segmented flow autoanalyzer for colorimetric detection of dissolved nutrients. The instrument is composed of 5 channels, an autosampler, 2 digital colorimeters, 2 high precision pumps, and a fluorometer.
Nitrate and Nitrite - Nitrate is reduced to nitrite by a copper-cadmium reductor column. The nitrite reacts with sulfanilamide under acidic conditions to form a diazo compound, then couples with N-1-naphthylethylene diamine dihydrochloride to form a purple azo dye.
Phosphate - Following the method of Murphy and Riley, the procedure for the determination of ortho-phosphate is based on the colorimetric method in which a blue color is formed by the reaction of ortho-phosphate, molybdate ion and antimony ion followed by reduction with ascorbic acid at an pH<1.
Silicate - The determination of soluble silicates is based on the reduction of silico-molybdate in acidic solution to molybdenum blue by ascorbic acid. Oxalic acid is introduced to the sample stream before the addition of ascorbic acid to minimize interference from phosphates.
Ammonia - The sample is reacted with o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) at 75°C in the presence of borate buffer and sodium sulfite to form a fluorescent species proportional to the ammonia concentration. The fluorescence is measured at 460 nm following excitation at 370 nm.
Total dissolved nitrogen - Samples are first digested in an autoclave using a reagent composed of boric acid, potassium persulfate and sodium hydroxide, then run through the nitrate channel.
Total dissolved phosphorus - Samples are first digested in autoclave using a reagent composed of boric acid, potassium persulfate and sodium hydroxide, then run through the phosphate channel.
IDEXX Quanti-Tray 2000
The IDEXX Quanti-Tray/2000 is a semi-automated quantification method based on the Standard Methods Most Probably Number (MPN) model. After addition of the Colilert-18 ONPG-MUG substrate to the sample, the sample is then poured into a Quanti-Tray 2000 tray and sealed. The tray is incubated at 35º ± 0.5ºC for 18-22 hours to metabolize Colilert-18’s nutrient indicator ONPG/MUG and then checked for color change from clear to yellow (presence of total Coliforms) and bluish fluorescence (presence of E coli). Results are reported in terms of the Most Probably Number (MPN) of organisms present. This number is an estimate of the mean density of coliforms in the sample. The test can detect total coliforms and E. coli in water at 1CFU/100ml within 22 hours with as many as 2 million heterotrophic bacteria/100 ml present. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has stated in writing that Quanti-Tray/2000 can be used for compliance testing.
IN THE NEWS
- Water Quality Testing Certificate Offered at UH Maui College, UH News, July 2019
- Water Quality Program Debuts at UHMC, Maui News, July 2019
- Mauiʻs First Water Testing Lab is Open, Maui News, Sept 2018
- Ka Wai Ola: The Living Water of Maui, USDA, Sept 2018
- https://www.nfwf.org/media-center/press-releases/papahanaumokuakea-research-and-conservation-fund-announces-1-million-grants-support-management-and
- https://www.hawaii.edu/news/2020/08/14/native-hawaiian-agriculture-sustainability/

REFERENCES
Armstrong, F.A.J., Sterns, C.R. and Strickland, J.D.H., 1967 Deep Sea Res. 14, pp. 381-389.
"The measurement of upwelling and subsequent biological processes by means of the Technicon AutoAnalyzer and associated equipment."
Grasshoff, K., Technicon International Congress, June 1969.
Federal Water Pollution Control Administration Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes, November 1969.
Methods of Seawater Analysis, K. Grasshoff et. al., Verlag Chemie, 2nd Edition, 1983.
J. Murphy and J.P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27:31-36.
L. Drummond and W. Maher, 1995. Re-examination of the optimum conditions for the analysis of phosphate. Analytical Chimica Acta 302: 69-74.
Methods of Seawater Analysis, K. Grasshoff, M. Ehrhardt, K. Kremling, second revised and extended edition, 1983
Fluorometric determination of ammonia in sea and estuarine waters by direct segmented flow analysis.
Kerouel, R, Aminot, A. Marine Chemistry Vol. 57, no. 3-4, pp. 265-275. Jul 1997.